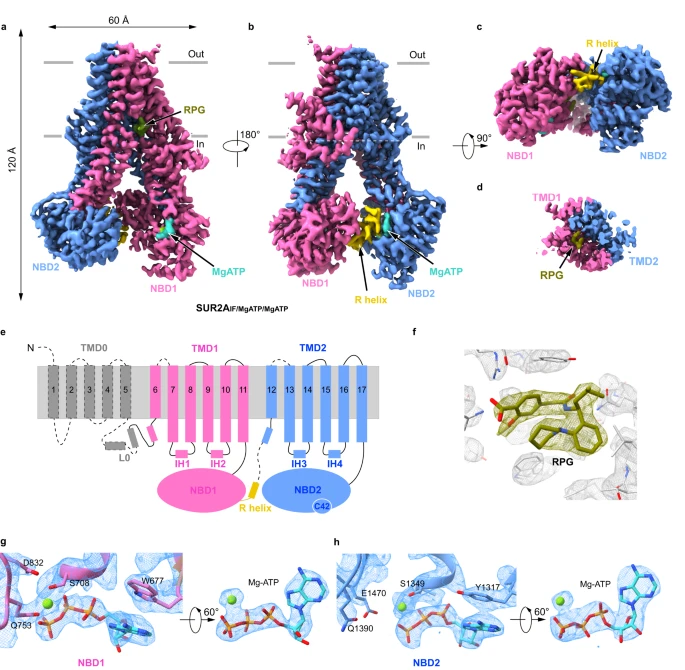
The inhibition mechanism of the SUR2A-containing KATP channel by a regulatory helix
KATP channels are metabolic sensors for intracellular ATP/ADP ratios, play essential roles in many physiological processes, and are implicated in a spectrum of pathological conditions. SUR2A-containing KATP channels differ from other subtypes in their sensitivity to Mg-ADP activation. However, the underlying structural mechanism remains poorly understood. Here we present a series of cryo-EM structures of SUR2A in the presence of different combinations of Mg-nucleotides and the allosteric inhibitor repaglinide. These structures uncover regulatory helix (R helix) on the NBD1-TMD2 linker, which wedges between NBD1 and NBD2. R helix stabilizes SUR2A in the NBD-separated conformation to inhibit channel activation. The competitive binding of Mg-ADP with Mg-ATP to NBD2 mobilizes the R helix to relieve such inhibition, allowing channel activation.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-39379-4